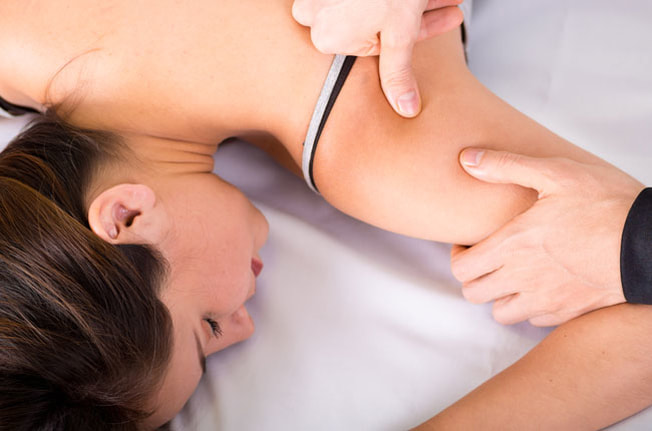
It is a common misconception that sports massage is only for elite athletes. While this type of treatment can improve the performance of an athlete it is also quite beneficial to anyone who suffers from chronic pain or has an injury, whether from running a marathon, playing tennis on the weekend, or working in the garden. When it comes to the musculoskeletal system, we all have the same anatomy. A sore muscle is a sore muscle regardless of what caused it!
Sports massage is designed to focus on muscles that have seen a large degree of stress and use almost overuse, releasing tension in the deeper layers of muscular tissue. The aim is to reduce pain, improve recovery between activities, increase mobility and to improve the overall functioning of the muscular system.
A typical session may involve deep tissue massage, trigger point therapy, stretching and muscle energy techniques to activate and lengthen the muscles and to increase range of motion which allows muscles to perform at their peak.
A sports massage can be used pre-event to increase blood flow to the muscles, improve flexibility and decrease the chance of injuries. It can also be used after a specific event or training to minimise recovery time, prevent stiffness, relieve pain and to return the muscles to their relaxed state.
Sports massage is a popular form of treatment for soft tissue injuries and can form part of many athletes injury prevention strategy. It can play an important part in the life of any sportsman or woman whether they are injured or not and has a number of benefits both physical, physiological and psychological. It can help maintain the body in generally better condition, prevent injuries and loss of mobility, cure and restore mobility to injured muscle tissue, boost performance and extend the overall life of your sporting career.
Sports Massage can be characterized two ways: pre-activity and post-activity massage. Pre-activity massage uses dynamic stretching to allow the connective tissue to work through a full range of motion, thereby reducing possible injury. Post-activity massage focuses on recovering the muscle tissue that may have been impacted doing the particular sport. It involves long strokes to flush out the toxins that causes soreness in the muscles and joints.
There are different types of sports massage based on when the massage is delivered in relation to competition:
Sports massage is designed to focus on muscles that have seen a large degree of stress and use almost overuse, releasing tension in the deeper layers of muscular tissue. The aim is to reduce pain, improve recovery between activities, increase mobility and to improve the overall functioning of the muscular system.
A typical session may involve deep tissue massage, trigger point therapy, stretching and muscle energy techniques to activate and lengthen the muscles and to increase range of motion which allows muscles to perform at their peak.
A sports massage can be used pre-event to increase blood flow to the muscles, improve flexibility and decrease the chance of injuries. It can also be used after a specific event or training to minimise recovery time, prevent stiffness, relieve pain and to return the muscles to their relaxed state.
Sports massage is a popular form of treatment for soft tissue injuries and can form part of many athletes injury prevention strategy. It can play an important part in the life of any sportsman or woman whether they are injured or not and has a number of benefits both physical, physiological and psychological. It can help maintain the body in generally better condition, prevent injuries and loss of mobility, cure and restore mobility to injured muscle tissue, boost performance and extend the overall life of your sporting career.
Sports Massage can be characterized two ways: pre-activity and post-activity massage. Pre-activity massage uses dynamic stretching to allow the connective tissue to work through a full range of motion, thereby reducing possible injury. Post-activity massage focuses on recovering the muscle tissue that may have been impacted doing the particular sport. It involves long strokes to flush out the toxins that causes soreness in the muscles and joints.
There are different types of sports massage based on when the massage is delivered in relation to competition:
- During the training programme (maintenance) – to correct soft tissue dysfunction
- Before competition (pre-event) – to aid preparation by loosening muscles
4 MAIN AREAS OF TIMING & TRAINING
BENEFITS OF SPORTS MASSAGE:
- Improved range of motion and muscle flexibility
- Reduced risk of injury
- Boosted circulatory system
- Helps shorten recovery time between workouts
- Can help prevent over-training
- Helps Eliminate By-Products of Exercise
- Psychological Benefits
- Reduces Pain
Effects of Massage
PHYSICAL EFFECTS:
PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS:
PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS:
- Pumping - The stroking movements suck fluid through blood vessels and lymph vessels and a vacuum is created that protects muscle tissue from damage.
- Increased tissue permeability - Helps with removal of waste products to encourage the muscles to take up oxygen and nutrients for quicker recovery.
- Stretching - Massage can stretch tissues that could not be stretched in the usual methods.
- Break down scar tissue - Scar tissue is the result of previous injuries or trauma and can effect muscle, tendons and ligaments.
- Improve tissue elasticity - Hard training can make tissues hard and inelastic, massage helps reverse this by stretching the tissues.
- Opens micro-circulation - Massage opens or dilates the blood vessels, stretching them to enable nutrients to pass through more easily.
PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS:
- Pain reduction
- Relaxation
PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS:
- Anxiety reduction
- Invigorating
CONTRAINDICATION OF SPORTS MASSAGE:
- Open wounds - Any cuts, lacerations or grazes.
- Muscle ruptures
- Tendon ruptures
- Muscle and tendon partial tears
- Contusions
- Burns, Chilblains and Broken
- Rheumatoid arthritis and gout
- Bursitis
- Myositis
- Infections of the skin and soft tissue
- Thrombosis
- Artificial blood vessels
- Bleeding disorders such as heamophillia
- Tumours





















